Kicking off with Understanding Marketing Attribution Models, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone american high school hip style that unfolds with each word.
When it comes to navigating the complex world of marketing, understanding attribution models is key. From first-touch to last-touch and everything in between, these models provide insights that can revolutionize your marketing strategy. So buckle up and get ready to dive deep into the world of marketing attribution.
Introduction to Marketing Attribution Models

Marketing attribution models are tools used by businesses to determine which marketing channels are contributing to customer conversions. These models help in understanding the effectiveness of different marketing efforts and allocating resources accordingly.
Popular marketing attribution models used in the industry include:
– First Touch Attribution: Gives credit to the first touchpoint that a customer interacts with before making a purchase.
– Last Touch Attribution: Attributes the conversion to the last touchpoint that led to the sale.
– Linear Attribution: Distributes credit equally among all touchpoints in the customer journey.
– Time Decay Attribution: Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion.
Understanding marketing attribution is crucial in comprehending the customer journey. It helps businesses identify which marketing strategies are driving sales, optimize campaigns, and allocate budgets effectively to maximize ROI.
Types of Marketing Attribution Models
Marketing attribution models are essential for understanding the impact of each touchpoint in the customer journey. Let’s dive into four common types of marketing attribution models.
First-Touch Attribution, Understanding Marketing Attribution Models
In first-touch attribution, all the credit for a conversion is given to the first touchpoint the customer interacted with. This model assumes that the initial touchpoint played the most significant role in influencing the customer’s decision to convert.
Last-Touch Attribution
Last-touch attribution, on the other hand, attributes all the credit to the final touchpoint before the conversion. This model focuses solely on the last interaction that led to the conversion, overlooking the impact of previous touchpoints.
Linear Attribution Model vs. Time-Decay Model
The linear attribution model evenly distributes credit across all touchpoints in the customer journey. This means that each touchpoint receives an equal share of the credit for the conversion. On the other hand, the time-decay model gives more credit to touchpoints that are closer in time to the conversion, assuming they had a more significant impact.
Position-Based Attribution Model
The position-based attribution model takes into account specific touchpoints in the customer journey and assigns varying amounts of credit based on their position. For example, it may give more credit to the first and last touchpoints, recognizing their importance in the conversion process.
Challenges in Implementing Marketing Attribution Models: Understanding Marketing Attribution Models
When it comes to implementing marketing attribution models, businesses often face a variety of challenges that can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of their marketing strategies. From cross-device tracking issues to the complexities of offline conversions, navigating these obstacles is crucial for success in today’s digital landscape.
Cross-Device Tracking
Cross-device tracking poses a significant challenge to marketing attribution models. With consumers using multiple devices throughout their purchasing journey, tracking their interactions across different platforms can be difficult. This can lead to inaccuracies in attributing conversions to the correct marketing channels, resulting in skewed data and ineffective decision-making.
Offline Conversions
Offline conversions, such as in-store purchases or phone orders, present another obstacle to digital attribution models. These conversions are often challenging to track and attribute to online marketing efforts, leading to gaps in data and incomplete insights into the customer journey. Without a comprehensive view of all touchpoints, businesses may struggle to optimize their marketing strategies effectively.
Best Practices for Effective Marketing Attribution
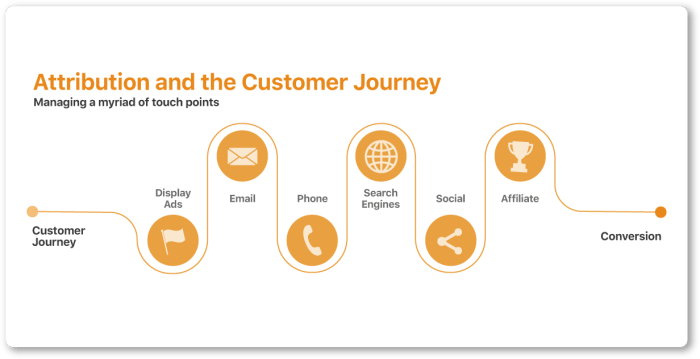
Effective marketing attribution requires a strategic approach that combines various models, ensures data accuracy, and leverages tools for successful implementation.
Combining Multiple Attribution Models
- Utilize a combination of first-touch, last-touch, and multi-touch attribution models to gain a comprehensive view of the customer journey.
- Assign different weightings to each touchpoint based on its impact on conversions to better understand the effectiveness of marketing channels.
- Consider using algorithmic attribution models that automatically adjust the credit given to touchpoints based on their influence.
Significance of Data Quality and Accuracy
- Ensure data accuracy by regularly monitoring and validating the sources of data used in attribution modeling.
- Implement data cleansing processes to remove any inconsistencies or errors that could skew attribution results.
- Invest in data analytics tools that can help track and analyze customer interactions across multiple touchpoints accurately.
Tools and Software for Effective Implementation
- Google Analytics: Provides insights into customer behavior and attribution across various marketing channels.
- Adobe Analytics: Offers advanced attribution modeling capabilities for a more in-depth analysis of customer journeys.
- HubSpot: Helps track and attribute conversions to specific marketing campaigns and channels, enabling better optimization strategies.